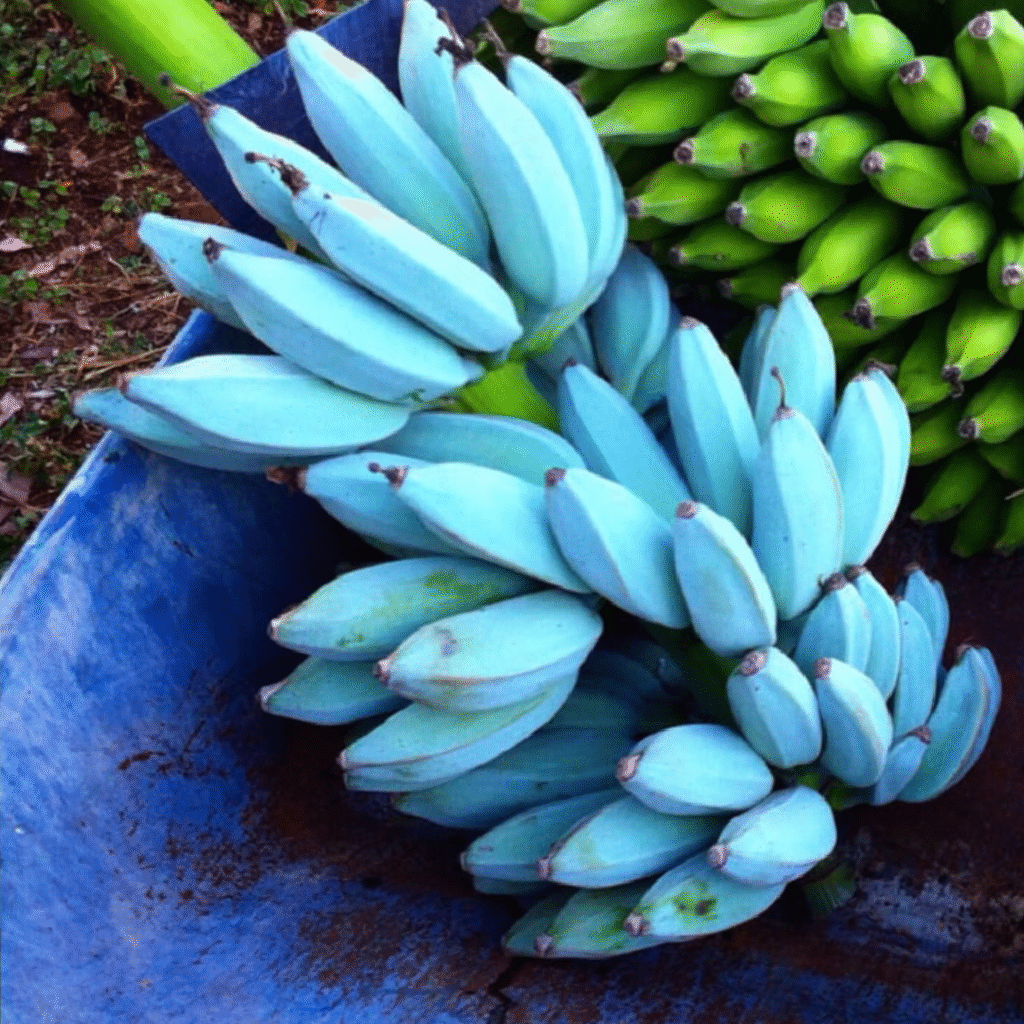
Bananas are one of the world’s most popular and widely consumed fruits, with countless varieties thriving in tropical and subtropical regions. Among these, the Blue Java banana stands out as one of the most unique and sought-after types, thanks to its striking blue-hued skin and creamy, vanilla-flavored flesh. Known affectionately as the “ice cream banana,” this exotic variety has captured the attention of gardeners, farmers, and culinary enthusiasts alike.
But which country produces the most Blue Java bananas in the world? In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating history, characteristics, cultivation practices, and global production data of Blue Java bananas — and reveal the country leading the charge in growing this special fruit.
What is the Blue Java Banana?
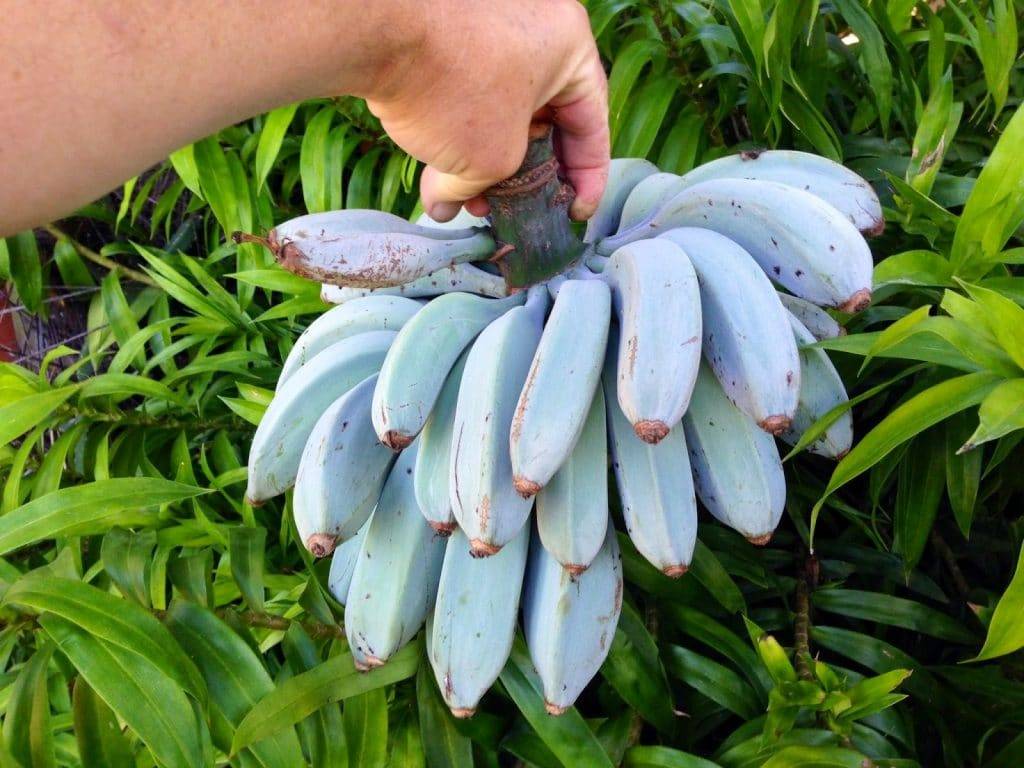

The Blue Java banana (Musa acuminata × balbisiana, ABB Group) is a hybrid cultivar known for:
- Unique appearance: Unripe fruits are covered in a powdery, silvery-blue skin that turns pale yellow when ripe.
- Flavor and texture: Soft, creamy, and custard-like flesh with a mild vanilla flavor, earning it the nickname “ice cream banana.”
- Cold hardiness: One of the few banana varieties capable of withstanding cooler temperatures down to about -6°C (21°F).
Native to Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands, the Blue Java banana has become a cherished heirloom fruit in many tropical countries.
Origins and History
The origins of the Blue Java banana trace back to Southeast Asia, particularly the Indonesian islands and Malaysia, where it has been cultivated for generations. Its ability to survive cooler climates made it especially valuable in mountainous regions and temperate areas where conventional banana varieties struggle.
Over time, Blue Java bananas spread across:
- The Philippines
- India
- Thailand
- Sri Lanka
- Hawaii
- Fiji
- Australia
- And parts of Central America and the Caribbean
Despite its appeal, Blue Java remained a relatively niche variety compared to the globally dominant Cavendish banana, largely due to its shorter shelf life and smaller-scale commercial cultivation.
Characteristics of Blue Java Bananas
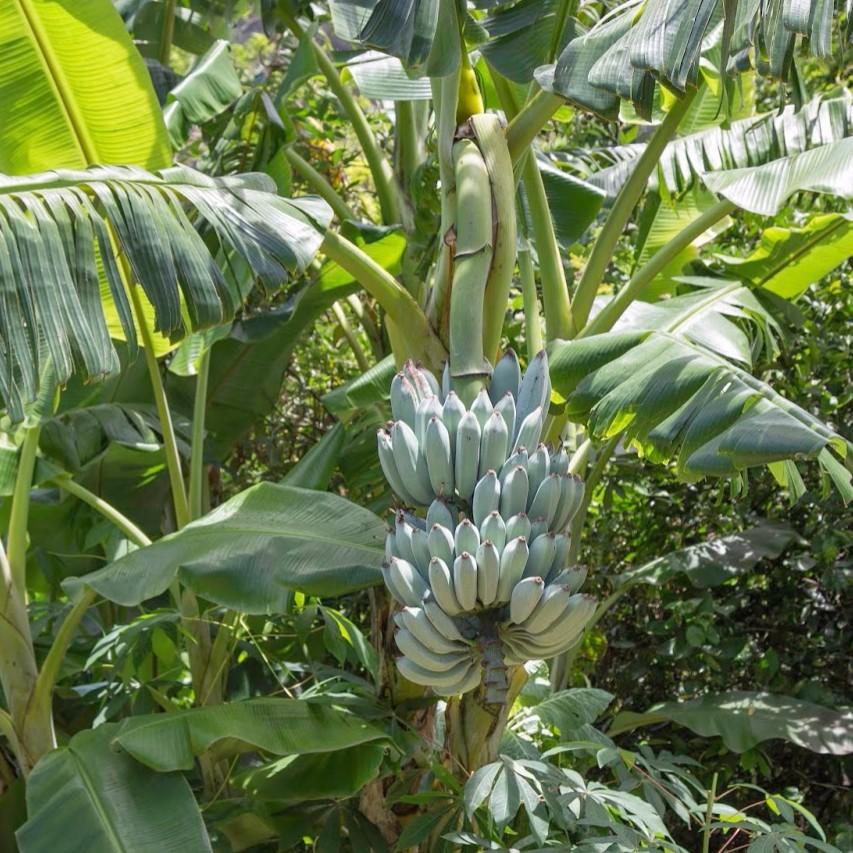

Here’s why Blue Java bananas are so distinctive:
Appearance:
- Unripe skin: Powdery, silvery-blue hue.
- Ripe skin: Pale yellow with soft, creamy white flesh.
Flavor:
- Described as a cross between vanilla custard and ice cream.
- Smooth, melt-in-the-mouth texture.
Growing Conditions:
- Thrives in tropical and subtropical climates.
- More cold-resistant than most bananas.
- Grows to a height of 4.5 to 6 meters (15 to 20 feet).
- Bears large bunches of 12–20 fruits each.
Uses:
- Eaten fresh.
- Blended into smoothies.
- Used in tropical desserts.
- Added to ice creams and baked goods.
Where is Blue Java Grown?
Today, Blue Java bananas are cultivated in several countries with warm, humid climates, including:
- Indonesia
- Malaysia
- The Philippines
- India
- Sri Lanka
- Hawaii (USA)
- Fiji
- Australia
- Central America
While many countries grow Blue Java bananas on a small scale for local consumption or specialty markets, a few nations lead in both commercial and domestic production.
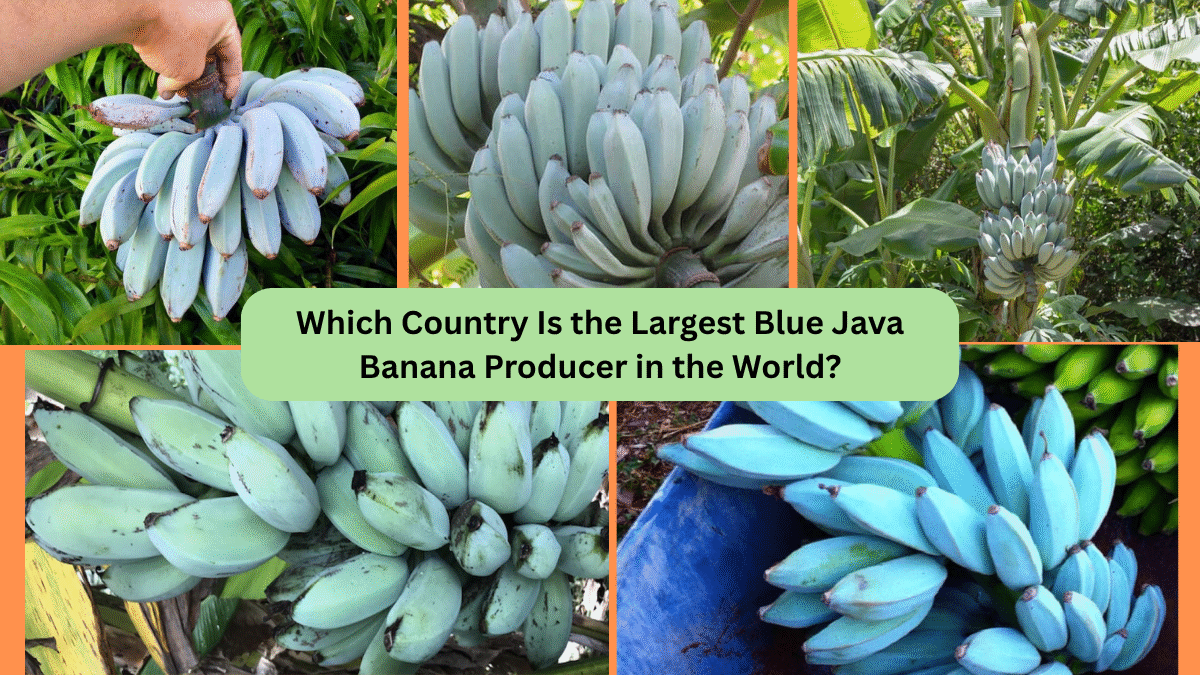
Which Country Is the Largest Blue Java Banana Producer in the World?
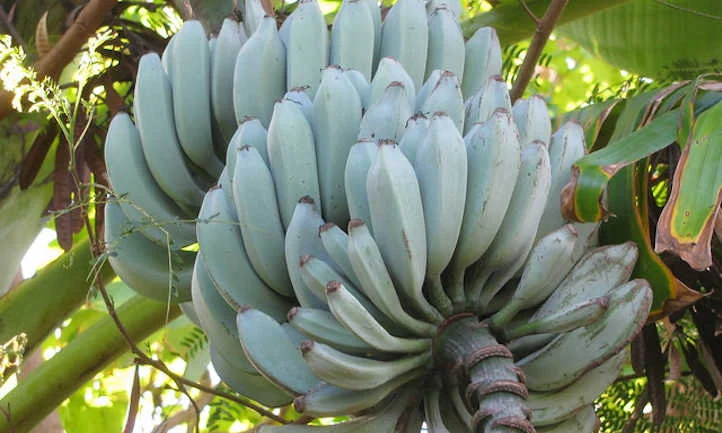

Based on cultivation history, production capacity, and current farming practices, Indonesia holds the title of the largest Blue Java banana producer in the world.
Why Indonesia Leads Blue Java Banana Production
Native Origin
Indonesia is the native home of the Blue Java banana, particularly on the islands of Java, Sumatra, and Bali. The banana has long been part of local agriculture, gardens, and traditional markets.
Ideal Climate
Indonesia’s tropical climate, rich volcanic soils, and consistent rainfall provide perfect growing conditions for Blue Java bananas.
Widespread Cultivation
In Indonesia, Blue Java bananas — known locally as “Pisang Raja Udang” or “Pisang Kipas” — are commonly grown in:
- Home gardens
- Smallholder farms
- Community orchards
- Local markets for fresh consumption and religious ceremonies
Export Potential
While the majority of Indonesian Blue Java bananas are consumed domestically, some are exported to neighboring countries like Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand, as well as limited quantities to specialty markets in the United States and Europe.
Estimated Production Figures
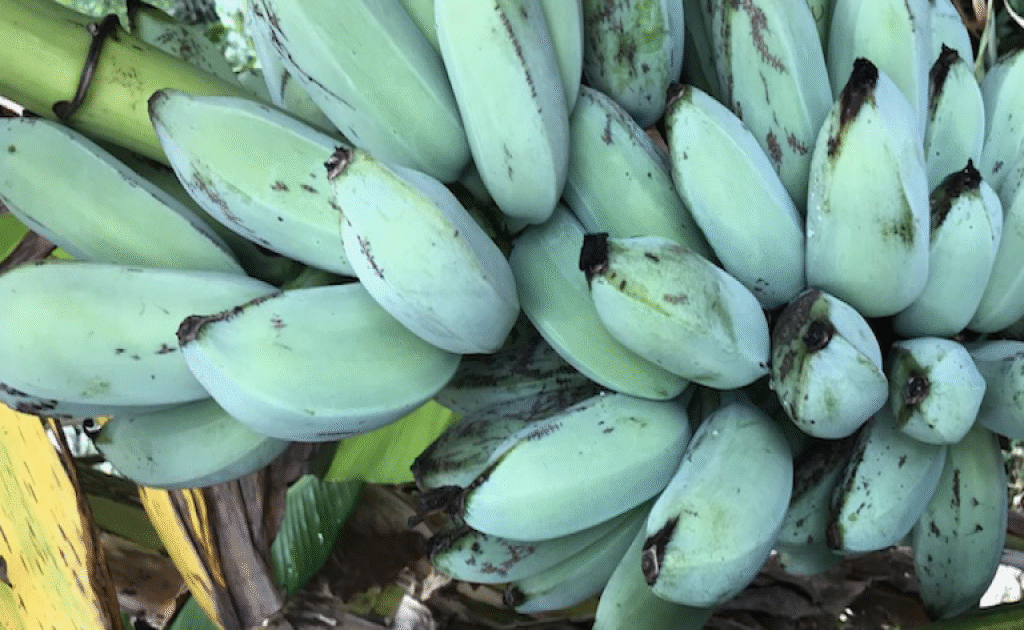

While exact, official production figures for Blue Java bananas are limited due to their classification under broader banana categories, agricultural experts and regional data suggest:
- Indonesia produces approximately 250,000 to 300,000 metric tons of Blue Java bananas annually.
- This makes Indonesia the undisputed leader in both area of cultivation and total yield.
Other Significant Producers
Malaysia
Malaysia also cultivates Blue Java bananas, particularly in rural areas of Peninsular Malaysia and Sabah. Known locally as “Pisang Lemak Manis” and “Pisang Nipah”, these bananas are grown for local consumption and small-scale exports.
The Philippines
In the Philippines, Blue Java bananas — called “Krie” or “Morado” in some regions — are popular backyard fruits but not produced on a significant commercial scale.
India
In India, interest in Blue Java bananas has grown, especially in the states of Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala, where farmers cultivate them as a climate-resilient alternative to Cavendish varieties.
Hawaii (USA)
Hawaii is one of the only regions in the United States where Blue Java bananas are cultivated commercially. Though production is small, demand from tourists and health-conscious consumers remains high.
Challenges Facing Blue Java Production
Despite its advantages, cultivating Blue Java bananas comes with challenges:
- Limited commercial scalability compared to Cavendish bananas.
- Shorter shelf life reduces export viability.
- Vulnerability to Panama Disease (though less so than Cavendish).
- Seasonal availability can cause price fluctuations in local markets.
The Future of Blue Java Bananas

As global demand for unique, heirloom, and climate-resilient crops grows, Blue Java bananas are poised to gain wider popularity. With their cold tolerance, distinctive flavor, and growing reputation as a gourmet fruit, these bananas could carve out a niche market beyond Southeast Asia.
Countries like India, Hawaii, and Australia are already expanding their Blue Java production, while Indonesia continues to lead in both tradition and volume.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Indonesia is the largest Blue Java banana producer in the world. With its ideal growing conditions, deep-rooted cultivation history, and widespread domestic use, Indonesia dominates the global landscape of Blue Java production. While other countries like Malaysia, the Philippines, India, and Hawaii also contribute, none match Indonesia’s scale and expertise.
As awareness of Blue Java bananas grows among culinary enthusiasts, organic markets, and tropical fruit lovers worldwide, this delicious “ice cream banana” will likely gain even greater global recognition — and Indonesia will remain its proud heartland.






Leave A Comment