In the world of berries, while blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries often steal the spotlight, there exists a hidden gem — the loganberry. Known for its deep red hue, complex flavor, and excellent nutritional profile, loganberries are gaining steady traction in global markets. Though relatively niche compared to other berries, loganberries hold particular value in gourmet, processing, and health-food industries.
But when it comes to international trade, which country imports the most loganberries? Based on recent trade data and market analyses, Germany stands as the world’s largest importer of loganberries, primarily in frozen form. This article dives deep into the details of global loganberry trade, market trends, and why Germany leads the world in loganberry imports.
What Are Loganberries?
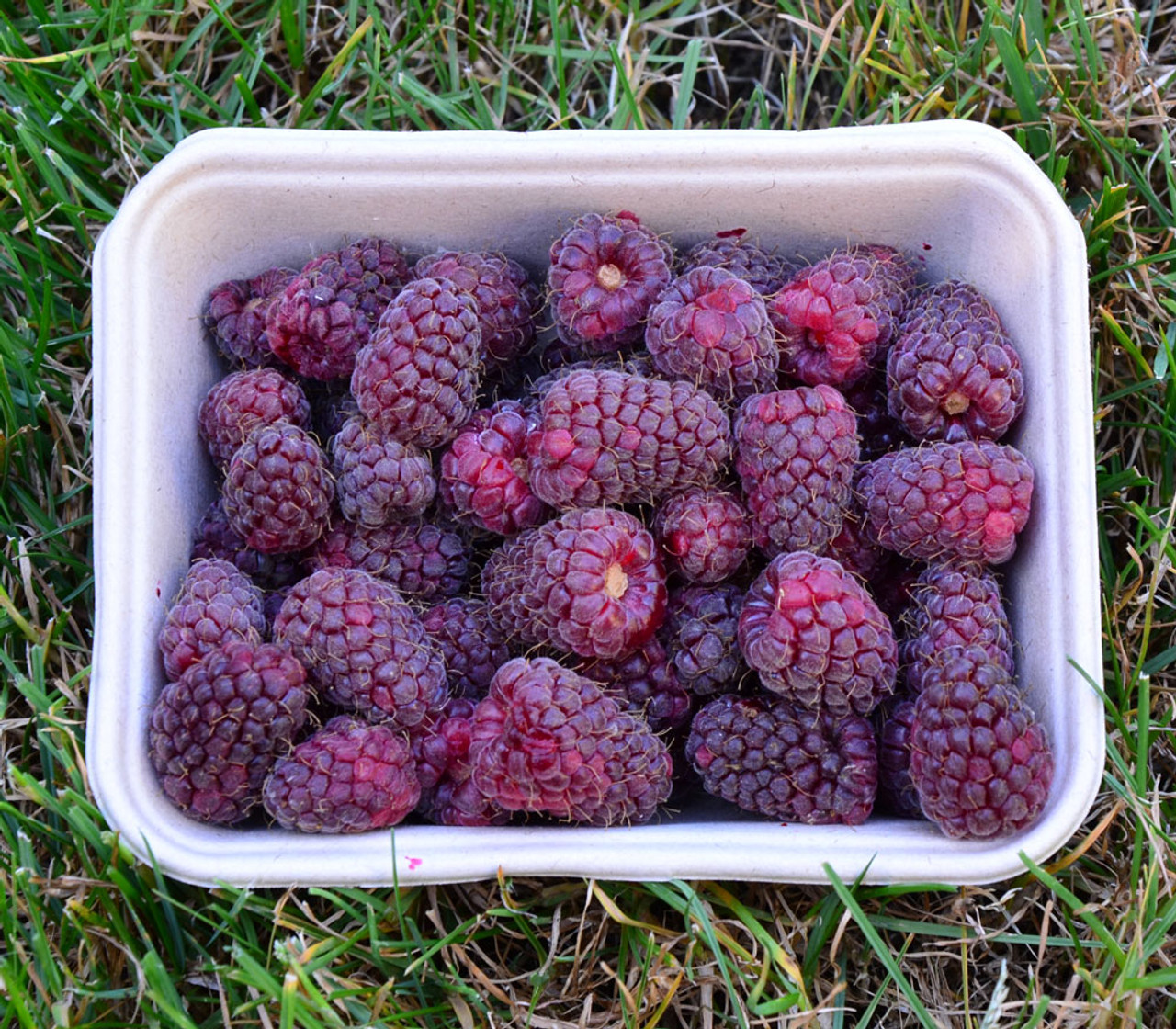

A natural hybrid between a blackberry (Rubus ursinus) and a raspberry (Rubus idaeus), loganberries were first developed in the 1880s by Judge James Harvey Logan in California. The berry boasts the deep coloring of a blackberry with the tart-sweet taste profile of a raspberry.
- Color: Deep crimson to dark purple
- Flavor: Sweet with a tangy, aromatic punch
- Texture: Juicy, firm skin, smaller drupelets than blackberries
- Uses: Popular in jams, pies, cordials, syrups, desserts, and as an antioxidant-rich functional ingredient
Though grown mainly in North America, the UK, New Zealand, and some parts of Eastern Europe, loganberry production remains limited — making international trade vital for fulfilling industrial and culinary demand in countries with limited local production.
The Global Market for Loganberries
Unlike more commercialized berries, loganberries are typically classified under the same Harmonized System (HS) codes as blackberries and raspberries, especially in the frozen category (HS Code: 081020). This makes exact data a challenge to isolate, but available trade reports on frozen berry imports offer reliable indicators of loganberry trade patterns.
Key Formats Traded:
- Frozen (Whole or Pureed) — most widely traded internationally
- Fresh — typically limited to local or short-distance exports due to perishability
- Processed — as jams, syrups, and juices
Key Exporting Countries:
- Poland
- Serbia
- Chile
- New Zealand
- United States
Which Country Is the Largest Loganberry Importer in the World?

According to FAO and UN Comtrade data, Germany is the world’s leading importer of frozen berries, a category that includes loganberries, raspberries, and blackberries.
In 2023:
- Germany imported approximately 117 million kilograms of frozen mixed berries (raspberries, blackberries, loganberries, and mulberries combined).
- This volume represents over 23% of total global imports in this category, making Germany the clear leader.
Considering that loganberries are typically exported in frozen form for food manufacturing and culinary use, Germany’s dominance in this sector strongly positions it as the top loganberry importer globally.
Why Is Germany the World’s Largest Loganberry Importer?
Several factors contribute to Germany’s market leadership:
A Thriving Food-Processing Industry
Germany has one of Europe’s largest food-processing sectors. The country’s bakeries, jam manufacturers, yogurt producers, and beverage companies incorporate significant quantities of imported berries—including loganberries—in their product lines.
Robust Consumer Demand for Berries
German consumers have a longstanding love for berries, both for their taste and health benefits. With a well-established health-conscious culture, Germany’s demand for antioxidant-rich fruits like loganberries remains consistently strong.
Year-Round Demand for Berries
Due to Germany’s limited domestic berry-growing season, imports—especially frozen—ensure a steady year-round supply to food manufacturers and retailers.
Cold-Chain Infrastructure Excellence
Germany has one of the most advanced cold storage and refrigerated logistics networks in Europe, facilitating large-volume imports of delicate fruits like loganberries while maintaining quality standards.
Central European Distribution Hub
Germany acts as a redistribution center for imported berries to neighboring countries like Austria, Switzerland, Netherlands, and Poland — further boosting import volumes.
Other Top Loganberry Importers

While Germany tops the list, other notable importers of frozen berries (including loganberries) include:
| Country | Estimated Annual Import Volume (2023) | Key Use Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | 117 million kg | Food processing, gourmet, retail |
| France | 45 million kg | Artisanal desserts, preserves |
| United States | 41 million kg | Food service, beverage industry |
| Belgium | 34 million kg | Frozen desserts, syrups |
| Russia | 33 million kg | Jams, juices, preserves |
France and the U.S. also have a healthy appetite for berries but lag behind Germany’s massive import volumes.
Where Are These Loganberries Coming From?
Top Exporting Nations to Germany:
- Poland — Europe’s largest frozen berry producer
- Serbia — Known for high-quality frozen berries
- Chile — Major off-season supplier from the Southern Hemisphere
- New Zealand — Premium quality berries including loganberries
- United States — Seasonal shipments, particularly frozen and pureed
Germany sources loganberries year-round by alternating between Northern and Southern Hemisphere suppliers.
Market Trends Fueling Demand
Several trends are driving Germany’s ongoing loganberry import growth:
- Health & Wellness Trends: German consumers favor berries for their antioxidant content and disease-fighting properties.
- Clean-Label and Organic Products: Increasing demand for organic, additive-free fruit products boosts specialty berry imports.
- Frozen Convenience: Frozen berries offer long shelf life and year-round availability for both industrial and household consumers.
- E-Commerce Expansion: Online grocery platforms are increasing accessibility to frozen berries for home cooks and health enthusiasts.
- Premium Desserts and Artisan Food Scene: Loganberries feature prominently in Germany’s artisan pastry, specialty jam, and craft beverage markets.
Challenges in Loganberry Trade

Despite robust demand, several challenges persist:
- Limited Global Production: Loganberries are not as widely grown as other berries, making supply limited.
- Data Classification Issues: Loganberries are often lumped with other berries in trade data, complicating precise tracking.
- Perishability: Fresh loganberries are delicate, requiring freezing to ensure quality for export.
- Climate Vulnerability: Changing weather patterns affect berry yields globally, creating supply uncertainties.
Future Outlook
Germany’s demand for loganberries and other specialty berries is expected to grow steadily:
- Sustained food-processing demand will keep Germany at the top of global import rankings.
- Organic and specialty product growth will fuel interest in loganberries for health-focused consumers.
- Innovations in cold-chain logistics and freezing technology will expand import capabilities.
- Emerging secondary markets in Europe like Austria and Switzerland may grow, with Germany acting as the primary gateway.
Final Verdict

Based on available data and trade patterns, Germany holds the title as the world’s largest importer of loganberries. The country’s thriving food-processing industry, health-focused consumer culture, advanced logistics, and year-round demand for frozen berries have placed it firmly at the top of the global import market for loganberries.
As global tastes evolve and awareness of specialty berries grows, Germany’s role as the primary destination for imported loganberries is poised to continue — ensuring this unique hybrid berry finds its way into the jams, pastries, desserts, and health products of Europe’s most berry-loving nation.