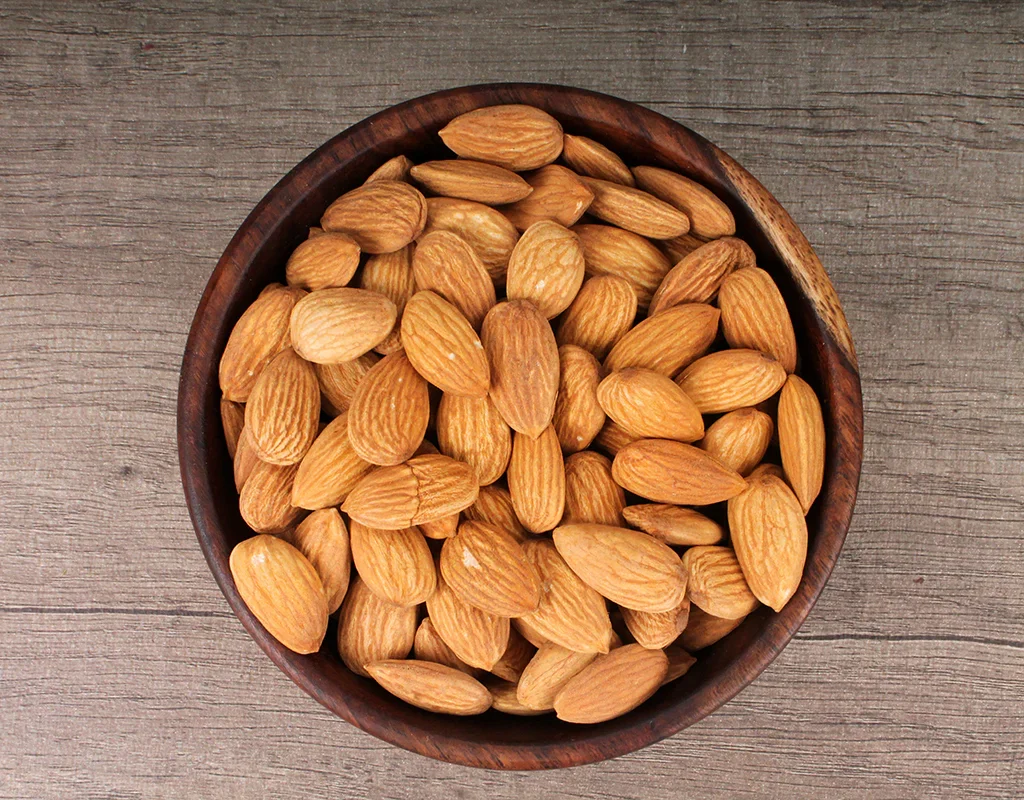
Almonds are among the world’s most loved and versatile tree nuts, celebrated not only for their crunchy texture and mildly sweet flavor but also for their nutritional richness. From snacking and baking to plant-based milk alternatives and gourmet dishes, almonds have earned their place in kitchens and diets around the globe.
While several countries produce and export almonds, one nation has long held the crown as the world’s largest almond exporter — the United States. In this article, we’ll delve into how the U.S. came to dominate the almond export market, who the other major players are, and what trends are shaping the global almond trade.
Global Almond Market Overview

Almonds are cultivated in various parts of the world, including the Mediterranean region, the Middle East, Australia, and the Americas. However, in terms of export volume and value, a handful of countries account for the vast majority of global almond trade.
There are two primary forms of almonds traded internationally:
- In-shell almonds (whole nuts with their shells intact)
- Shelled almonds (kernels removed from their shells)
Both categories have significant markets, though shelled almonds often dominate due to their ease of use in consumer and industrial food production.
The United States: Undisputed Leader in Almond Exports
The United States, specifically the state of California, is by far the world’s largest almond exporter. According to the latest data from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) and international trade reports:
- The U.S. accounts for over 65-70% of the global almond export market by value.
- In 2023, U.S. almond exports reached a value of approximately $4.2 billion.
- California alone produces about 80% of the world’s total almond supply and 100% of U.S. commercial almond output.
Major Almond Export Destinations from the U.S.
The United States exports almonds to more than 100 countries, with the following being the top markets:
- India
- European Union (Germany, Spain, France)
- China
- United Arab Emirates
- Japan
India has become the largest importer of U.S. in-shell almonds, driven by the nut’s popularity in Indian festivals and daily consumption. Meanwhile, Europe remains a key market for shelled almonds, especially for the confectionery, bakery, and snack industries.
Why the U.S. Leads the Almond Export Market
Several factors contribute to the U.S.’s dominance in almond exports:
- Ideal Growing Conditions: California’s Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters is perfect for almond orchards.
- Extensive Infrastructure: Highly mechanized farming, state-of-the-art processing facilities, and efficient logistics support large-scale production and global distribution.
- Advanced Research & Development: Organizations like the Almond Board of California promote sustainable farming practices, improve crop yields, and expand market access worldwide.
- Established Trade Relationships: Decades of strong trade agreements and market development efforts have opened doors in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Spain: Europe’s Leading Almond Exporter

While the U.S. dominates globally, Spain holds the title of Europe’s largest almond exporter and typically ranks second in the world.
- In 2023, Spain exported approximately $530–$550 million worth of almonds.
- Key export destinations include Germany, France, Italy, and the United Kingdom.
- Spain produces both conventional and organic almonds, with an increasing share of premium, pesticide-free, and sustainably grown varieties.
Spain’s almond industry thrives due to:
- Centuries-old cultivation traditions.
- Strong demand within the European Union.
- A focus on high-value, specialty almond varieties like Marcona almonds, prized for their flavor and texture.
Australia: A Fast-Growing Almond Exporter
Australia has rapidly expanded its almond industry in recent decades and now ranks third globally.
- In 2023, Australian almond exports reached about $490 million.
- Primary markets include India, China, United Arab Emirates, and Japan.
Australia benefits from:
- Modern, efficient almond orchards concentrated in regions like Sunraysia, Riverina, and Riverland.
- A counter-seasonal advantage — while northern hemisphere producers harvest between August and October, Australia’s almonds are harvested between February and April.
- Strategic trade agreements with Asian markets, which are experiencing rising demand for healthy, plant-based foods.
Other Notable Almond Exporters

While the United States, Spain, and Australia lead the global almond trade, a few other countries make meaningful contributions:
- Turkey: Rapidly growing as a regional supplier, particularly to Middle Eastern markets.
- Iran: Historically significant, though its exports fluctuate due to political and trade restrictions.
- Morocco, Italy, and Tunisia: Known for specialty almond varieties used in traditional Mediterranean cuisine.
Global Almond Export Trends
The global almond export market is evolving, driven by several key trends:
Rising Health Awareness
Consumers worldwide are increasingly seeking healthy, plant-based, and protein-rich snacks, boosting almond consumption.
Growth in Plant-Based Foods
Demand for products like almond milk, almond butter, and gluten-free almond flour has surged in recent years.
Expanding Asian Markets
India, China, and Japan are experiencing strong growth in almond imports, particularly in urban centers where Western dietary trends are gaining traction.
Sustainability Focus
Water usage in almond farming, especially in drought-prone California, has come under scrutiny. The U.S. industry is investing in water-efficient irrigation systems, pollinator-friendly practices, and environmental stewardship programs.
Tariff Challenges
Trade tensions and tariffs, particularly between the U.S. and China, have affected almond export flows, creating opportunities for other suppliers like Australia and Turkey.
Challenges Facing Almond Exporters

Even with rising global demand, almond exporters face several challenges:
- Climate change and water scarcity affecting yields and farm viability.
- Trade barriers and tariffs impacting access to key markets.
- Logistical hurdles, including container shortages and shipping delays.
- Increasing competition from emerging producers and other plant-based protein sources.
Conclusion: The Global Almond Export Leader

So, to answer the question: Which country is the largest almond exporter in the world?
Without a doubt, the title belongs to the United States, which commands around 70% of global almond export value. Its dominance is powered by California’s ideal growing conditions, highly efficient infrastructure, and well-established global market relationships.
Spain and Australia hold their own as significant exporters, with Australia in particular growing rapidly in Asia-Pacific markets. As health-conscious consumers seek more plant-based options and global culinary trends incorporate almonds into everything from snacks to fine dining, the worldwide almond trade will continue to thrive — with the U.S. remaining the leader for the foreseeable future.